Show table of content Hide table of content
The African continent is undergoing a remarkable geological transformation that has captivated scientists and researchers worldwide. Recent studies suggest that a new ocean basin may be forming in East Africa at an astonishing pace, challenging previous estimates and raising intriguing questions about the future of the continent’s landscape.
Rapid tectonic activity reshaping Africa’s geography
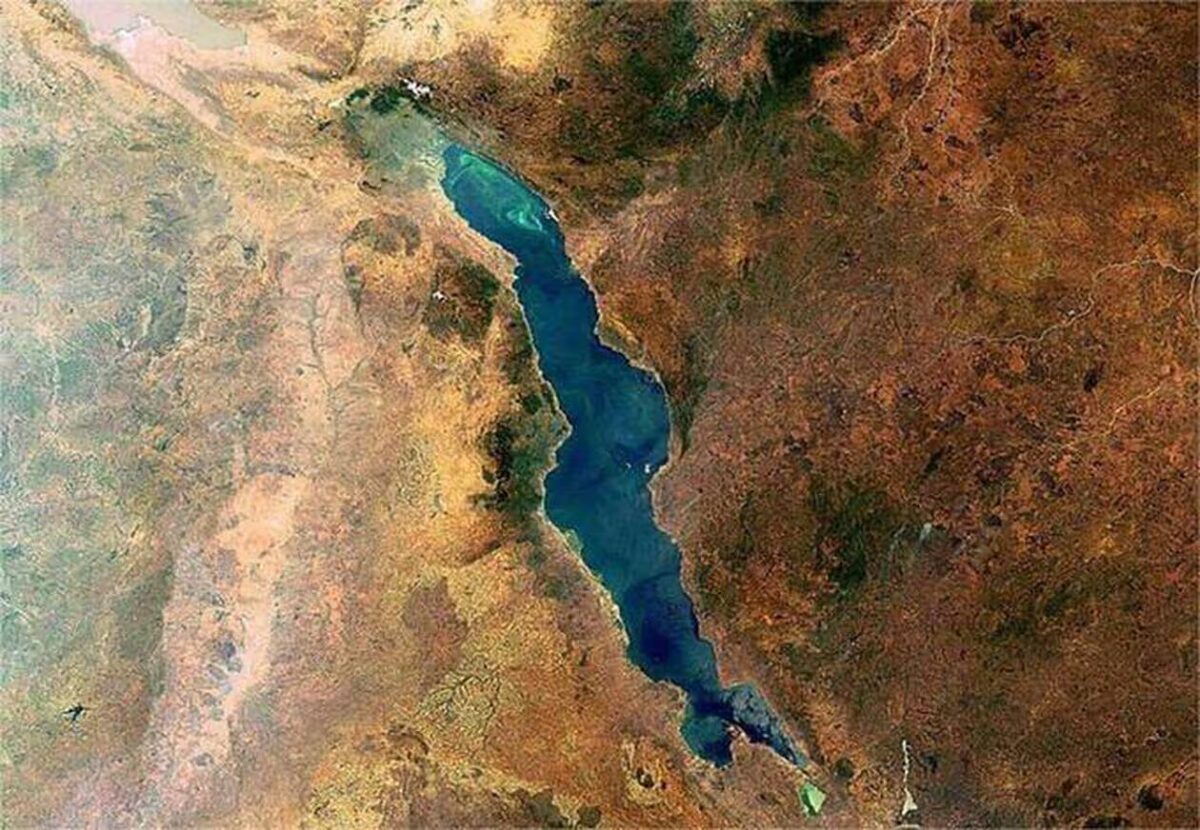
The East African Rift System, a vast network of faults and valleys stretching from Mozambique to the Red Sea, is the focal point of this dramatic geological change. Scientists have observed that two tectonic plates, the African and Somali plates, are gradually moving apart at a rate of approximately 0.8 centimeters per year. This continental drift is creating a massive rift that could eventually lead to the formation of a new ocean.
Cynthia Ebinger, a renowned geoscientist from Tulane University, has been studying this phenomenon since the 1980s. Her recent findings have challenged previous timelines, suggesting that the formation of a new ocean could occur much sooner than initially anticipated. “We’ve reduced the timeframe to about 1 million years, possibly even half that,” Ebinger stated in an interview with BBC Brazil.
The potential for accelerated change due to seismic events adds another layer of complexity to this geological puzzle. As Ebinger explains, “A major earthquake could further expedite the process, although current scientific methods cannot precisely predict such occurrences.”
Geological events shaping the future ocean
In 2005, a series of 420 earthquakes shook a desert region in Ethiopia, marking a significant seismic event for the continent. This activity resulted in the formation of a fissure in the Afar region, a process that would typically take centuries but occurred in just a matter of days. This rapid development has led scientists to reconsider their understanding of geological timescales.
The East African Rift now extends approximately 60 kilometers in length and reaches depths of up to 10 meters in the Ethiopian desert. This region, known for its extreme climate, experiences temperatures reaching 50 degrees Celsius and often goes without rainfall for up to nine months at a time. These harsh conditions provide a unique backdrop for the ongoing geological transformation.
The formation of this new ocean basin bears striking similarities to the birth of the Atlantic Ocean millions of years ago. Scientists studying the phenomenon have noted that this is the only place on Earth where continental crust is actively transitioning into oceanic crust, providing a rare opportunity to observe this process in real-time.
Implications of a changing African landscape
The potential formation of a new ocean in East Africa could have far-reaching consequences for the continent’s geography and ecosystems. Countries such as Zambia and Uganda, currently landlocked, might eventually gain coastlines, fundamentally altering their economic and environmental landscapes.
This geological shift is not only reshaping the physical terrain but also challenging our understanding of Earth’s dynamic processes. The rapid pace of change observed in East Africa serves as a reminder of the ever-evolving nature of our planet and the need for continued scientific exploration and monitoring.
To better understand the potential timeline for this geological transformation, scientists have compiled data on the movement of tectonic plates in the region:
Tectonic Plate Annual Movement Projected Movement (100 years) African Plate 0.8 cm 80 cm Somali Plate 0.8 cm 80 cm
While these movements may seem small on an annual basis, their cumulative effect over thousands or millions of years is substantial enough to reshape continents and create new ocean basins.
Scientific challenges and future research
The accelerated timeline for the formation of a new African ocean presents both opportunities and challenges for the scientific community. Researchers are faced with the task of:
- Developing more accurate models to predict geological changes
- Improving techniques for monitoring seismic activity in the region
- Studying the potential environmental impacts of a new ocean basin
- Assessing the socio-economic implications for affected countries
These research endeavors require a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from geology, oceanography, climate science, and social sciences as we see there. The strategies employed by scientists to tackle these complex issues demonstrate the innovative spirit driving modern geological research.
As our understanding of this phenomenon grows, so too does our appreciation for the dynamic nature of Earth’s geology. The formation of a new ocean in East Africa serves as a powerful reminder that our planet is in a constant state of flux, with changes occurring on timescales both vast and surprisingly brief.
While the exact timeline for the emergence of this new ocean remains uncertain, the ongoing research in East Africa continues to challenge our perceptions and expand our knowledge of Earth’s geological processes. As scientists work to unravel the mysteries of this fascinating phenomenon, they are not only solving complex puzzles but also providing valuable insights into the future of our planet’s geography.
The potential formation of a new ocean in Africa serves as a testament to the ever-changing nature of Earth’s surface. It reminds us that even seemingly permanent features of our planet are subject to transformation over geological timescales. As research continues, scientists and the public alike eagerly await new discoveries that will further illuminate this extraordinary process unfolding beneath our feet.
News 20 years ago, Steve Jobs explained how to succeed in life with a simple mindset.